Password vs. Passphrase: A Comprehensive Overview
We've all been told to create "strong" passwords, leading most of us to jam a capital letter, a number, and a symbol into a word, like P@ssword1!. But in today's world, that's like putting a basic screen door on a bank vault.
The truth is, the way we think about passwords is outdated. It's time to upgrade our strategy from simple passwords to more robust passphrases. For a complete overview of modern digital defense, you can also read our ultimate guide to password security.
So, what’s the difference between a password and a passphrase, and which one should you be using to protect your digital life? Let's break it down.
Table of Contents
What is a Password?
A password is what we traditionally use: a single string of characters, typically 8-16 characters long, that mixes letters (uppercase and lowercase), numbers, and symbols to verify your identity.
Example: Tr0ub4dor&3
What is a Passphrase?
A passphrase is a sequence of multiple, often random, words that form a longer but more memorable authentication secret. It relies on length to provide its security.
Example: Correct-Horse-Battery-Staple
Password vs. Passphrase: A Quick Comparison
| Feature | Password | Passphrase |
|---|---|---|
| Structure | A single, complex string of characters | A sequence of multiple words |
| Typical Length | 8-16 characters | 16-30+ characters |
| Memorability | Difficult to remember | Easy to remember |
| Security | Security comes from character complexity | Security comes from extreme length |
The Head-to-Head Battle: Which is Better?
While both can be effective, passphrases hold a significant advantage in the two areas that matter most: security and memorability.
Winner: Security - Passphrase
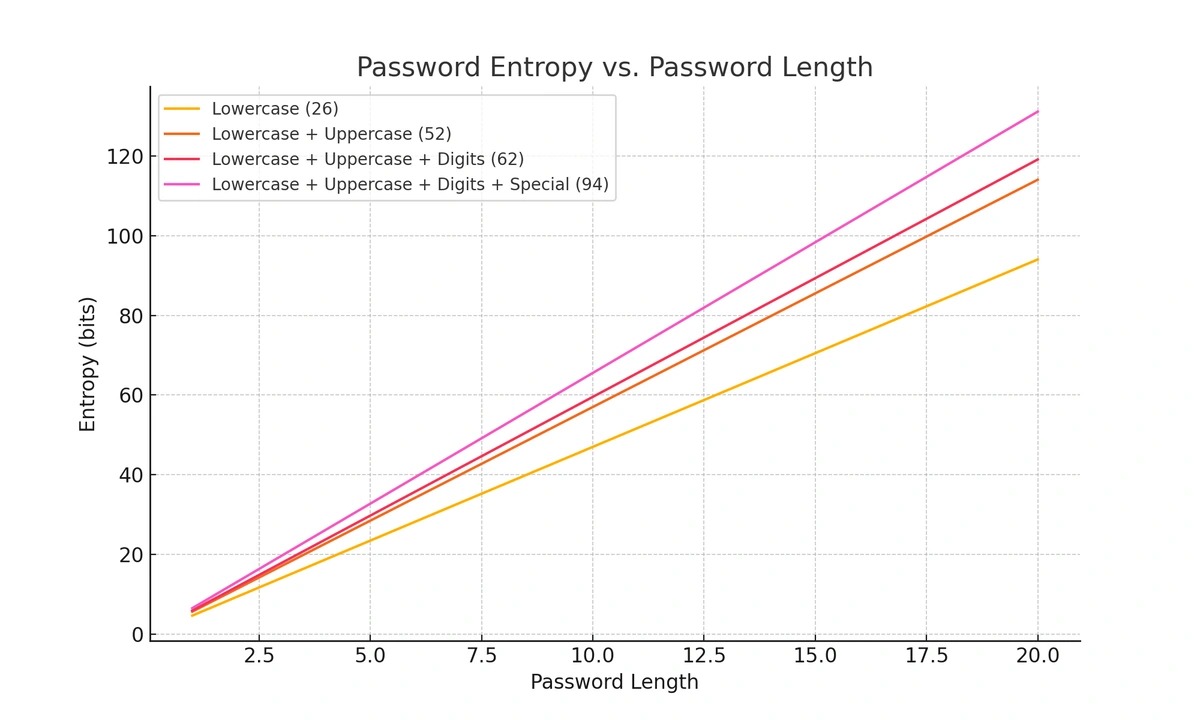
A computer's primary method for cracking passwords is a brute-force attack, where it tries every possible character combination. A short, complex password like R7!b*Pl9 is much easier for a computer to guess than a long passphrase like BlueGuitarSunsetOcean.
This is because adding length increases the password's "entropy" (randomness) exponentially, making it trillions of times harder to crack. The famous XKCD webcomic illustrated this perfectly: it would take a computer centuries to guess four random common words, while it could guess a typical complex 8-character password in days.
Winner: Memorability - Passphrase
Which is easier for you to remember: qZ5&pW@2 or ArcticMonkeyFuzzyBlanket?
The human brain isn't designed to remember random strings of characters, which is why so many people write down passwords or reuse them—both terrible security practices that leave them vulnerable to attacks like credential stuffing. A passphrase of four random words is simple to recall and type, eliminating the main cause of weak password habits.
When is a Password Still Necessary?
In some rare cases, a randomly generated password is your only option. This is primarily when a system has a strict character limit (e.g., a maximum of 12 characters) or doesn't allow spaces. In this scenario, using a free password generator to create a highly complex, random password is more secure than a two-word passphrase.
How to Create a Genuinely Strong Passphrase
Creating a secure passphrase is easy. Just follow the four-word random method.
- Think of four simple, random words. They should have no logical connection to each other or to you personally. Avoid famous quotes, song lyrics, or personal details.
- Combine them. You can separate them with spaces or hyphens.
ForestBicycleLoudLampShiny-Whale-Coffee-Planet
- (Optional) Add Complexity. To boost security even further for your most critical accounts (like email or banking), you can add a number or symbol.
ForestBicycleLoudLamp7Shiny-Whale-Coffee-Planet!
This simple method creates a passphrase that is easy for you to remember but nearly impossible for a machine to guess.
4 Essential Rules for Account Security
- Make it Long: Aim for a minimum of 16 characters. The longer, the better.
- Make it Unique: Never reuse a password or passphrase across multiple accounts. If one account is breached, attackers won't be able to access your others.
- Use Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA): Always enable a second layer of security. Understanding the difference between 2FA vs MFA is key to protecting your accounts even if your password is stolen.
- Use a Password Manager: It's impossible to remember dozens of unique, long passphrases. A password manager does the work for you, creating and storing them securely.
Never Forget a Passphrase Again with TeamPassword
Passphrases are the clear winner for protecting your accounts, but managing a unique one for every login is a challenge. That's where TeamPassword comes in.
You'll never have to remember over 100 unique passphrases. With a password manager, you only need to remember one strong master password, and we handle the rest.
- Centralized Password Management: Securely store and manage all your team's passphrases in one encrypted vault.
- Ironclad Security: Protect your data with advanced end-to-end encryption.
- Effortless Collaboration: Share access with your team without ever revealing the actual passphrase.
- Comprehensive Auditing: Track all password activity for complete accountability.
Try TeamPassword for free today!
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
1. Are passphrases really more secure than complex passwords?
Yes, overwhelmingly. A passphrase's length makes it exponentially more difficult for a computer to crack via brute-force attacks compared to a shorter, complex password. According to NIST guidelines, length is the most critical factor in password strength.
2. Should I use spaces in my passphrase?
If the website allows it, yes. Using spaces or hyphens increases the character set and length, adding to the overall security.
3. Isn't a passphrase just a long password?
Technically, yes. The term "passphrase" is used to encourage a different creation method: combining words for length and memorability, rather than creating a short, complex, and forgettable string of characters.